During a recent pentest, I needed to throw together a macOS virtual machine. Although there was lots of guides around the web, none seemed to work from start to finish. This post contains the steps I extracted from various resources in order to get a fully working High Sierra install within VirtualBox 5.
- Macos Virtualbox Linux
- Macos Virtualbox Audio
- Virtualbox Mac Os Github Update
- Virtualbox Mac Os Install
- Macos Guest Virtualbox Github
- Macos Virtualbox Github
- Virtualbox Mac Os Github Downloads
Step 1: Download The High Sierra Installer

To do this, you need to be on an existing macOS system. I was unable to find the download within the App Store itself, but following this link opened the App Store at the correct page: https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/macos-high-sierra/id1246284741?mt=12
MacOS: Virtualbox & VMware Supported Provisioners. Virtualbox; A licensed copy of VMware Fusion The VMWare Desktop Vagrant plugin is $79 and is required to use Vagrant with VMware. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please open an issue on the DetectionLab GitHub! Use geerlingguy’s script to prepare a sierra iso file. Git clone cd macos-virtualbox-vm chmod +x prepare-iso.sh./prepare-iso.sh /Applications/Install macOS Sierra.app /Users/suzy/sierra.iso.
After opening the aforementioned page in the App Store, start the download, but cancel the installation when it starts.
You can then verify that the installer has been downloaded by checking that '/Applications/Install macOS High Sierra.app' exists.
Step 2: Create a Bootable ISO
Next, you need to create an ISO from the installer application that was downloaded in step 1.
Running the below commands will create an ISO on your desktop named HighSierra.iso:
Step 3: Creating the Virtual Machine
I experimented with a few different settings in regards to the CPU and RAM allocation. I didn’t find a combination that didn’t work, but create a VM with the following things in mind:
- Ensure the name of the VM is
MacOS(ensure to keep the same casing) - Ensure the type is
Mac OS Xand the version ismacOS 10.12 Sierra (64-bit)(there is a High Sierra option too, but I chose Sierra by accident and it worked) - Untick
FloppyinSystem > Motherboard > Boot Order - Use >= 4096 MB of memory in
System > Motherboard - Use >= 2 CPUs in
System > Processor - Use 128 MB of video memory in
Display > Screen - Optionally enable 3D acceleration in
Display > Screen - Remove the IDE device in
Storage > Storage Devicesand replace it with a SATA controller - Add a new hard disk device under the SATA controller with >= 60 GB of space
- Ensure an optical drive is present under the SATA controller and mount the previously created ISO to it
- Untick the
Enable Audiooption underAudio
After creating the virtual machine with the above configuration, hit OK and exit the settings screen. Now, a number of extra options need to be set.
If you’re on Windows, you’ll need to cd into the appropriate directory under the VirtualBox installation path to run VBoxManage. For Linux users, this should be in your PATH variable already:
After running the above commands, the VM should be ready to boot!
Macos Virtualbox Linux
Step 4: Installation
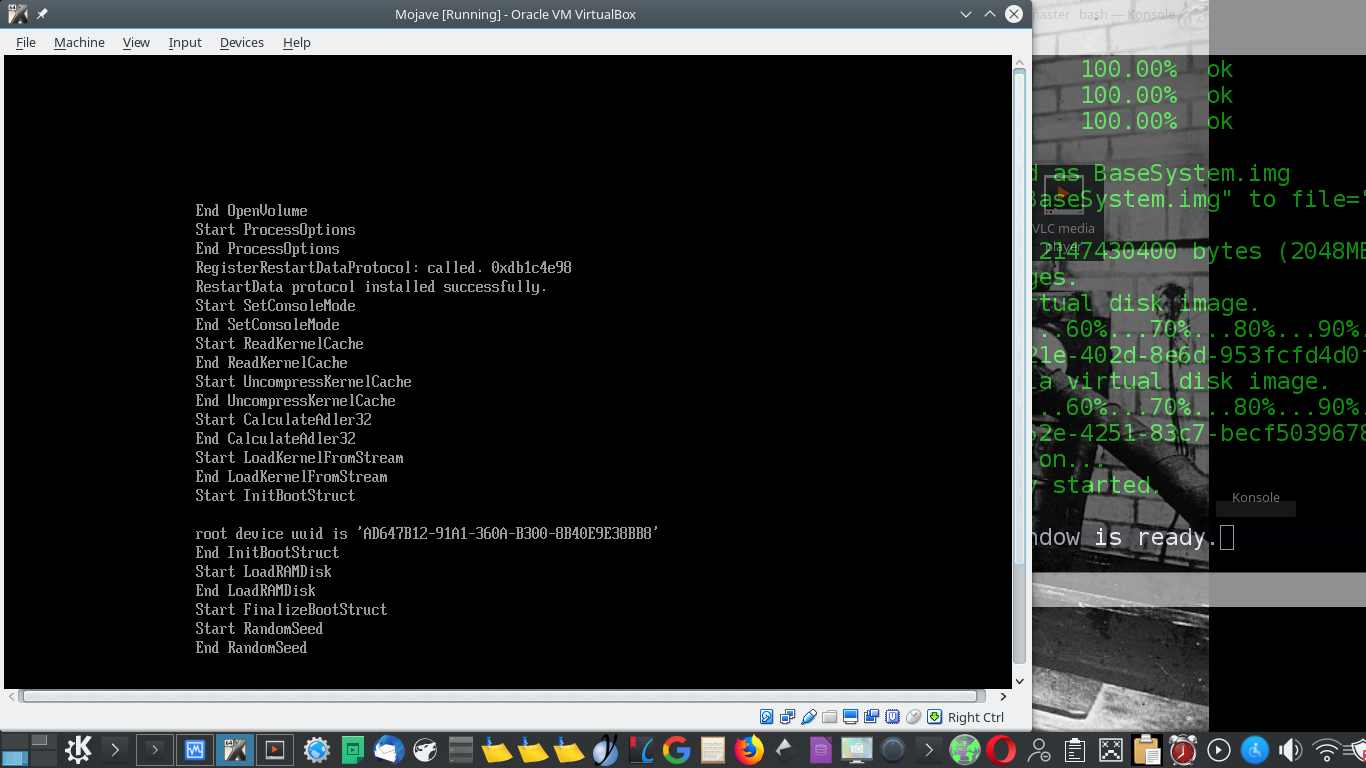
This is where near enough everything I read stopped, despite there being one more problem in the way - UEFI.
Boot into the VM, go into Disk Utility and erase the virtual disk that you added to the machine.
Macos Virtualbox Audio
After erasing the disk, start the installation procedure. After a short amount of time, it will reboot the VM.
Once it reboots, it’s going to boot back off the ISO again, once it’s done this, just shutdown the VM and eject the disk [the ISO] and then start the VM again to boot from disk.
On the next boot, it should boot into the installer that was copied to disk, but instead, you will be presented with a UEFI shell like below:
To continue the macOS installation, follow these steps:
Virtualbox Mac Os Github Update
- Type
exitand hit return - Select
Boot Maintenance Managerand hit return - Select
Boot From Fileand hit return - You will see two partitions, select the second partition and hit return
- Select
macOS Install Dataand hit return - Select
Locked Filesand hit return - Select
Boot Filesand hit return - Select
boot.efiand hit return
After following these steps, you will boot into the remainder of the macOS installation. From here, just follow the steps as per a regular macOS installation.
Virtualbox Mac Os Install
The next time you boot your virtual machine, you will not have to go through the UEFI shell; it should work without any further problems.
Step 5: Tweaking The Resolution
As there is no VirtualBox additions for macOS, the screen resolution won’t automatically change. If you know what resolution you wish to use, however, you can set it manually.
Ensure the virtual machine is powered off, and then run the following command; replacing 1920x1080 with whatever resolution you would like to use:
After running the above command, the next time you boot the machine, it will use the resolution specified.
Macos Guest Virtualbox Github
Now, you should have a fully working macOS virtual machine!
Macos Virtualbox Github
References
Virtualbox Mac Os Github Downloads
The information found in this post was pieced together from the following sources:
