Because a reasonably high dose of estrogen is taken from day 2 of your cycle in an FET protocol, the hormone is a down-regulator and prevents ovulation. A typical FET Debye length is approximately 5 nm at room temperature. To meet the requirement of the Debye length, biorecognition events must occur within 5 nm. Adobe reader mac gratis. As the height of an aptamer is generally less than 5 nm, aptamers are well-suited for use as biorecognition probes in FET biosensors.
FET Applications:
What are the various applications of the Field Effect Transistor?
In this short post let us discuss about the various applications of FET - Field Effect Transistor. Before proceeding further it is good to refresh about the basics of FET.
The Field Effect Transistor (FET) is a semiconductor device which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. Thus it is called as FET.
There are two types FET
- Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) or simply FET.
- Insulated Gate Field Effect Transistor IGFET.
It is also called as Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) transistor or MOSFET.
Applications of Field Effect Transistor (FET):
- FET has high input impedance and low output impedance. So it is used as a buffer in measuring instruments, receivers.
- FET has low noise operation. So it is used in RF amplifiers in FM tuners and communication equipment.
- FET has low input capacitance, so it is used in cascade amplifiers in measuring and test equipment.
- Since FET is a voltage controlled device, it is used as a voltage variable resistor in operational amplifiers and tone controls.
- FET has low inner modulation distortion. So it is used in mixer circuits in FM and TV receivers, and communication equipment.
- Since it is low-frequency drifts, it is used in oscillator circuits.
- FETs are used in low-frequency amplifiers in hearing aids and inductive transducers, as the coupling capacitor is small.
- Since FET occupying less space and easy to fabricate, it is used in digital circuits in computers, LSD and memory circuits.
Thanks for reading about Applications of FET.. Please leave your comments below.. Please subscribe to get more posts to your mail ID..
You May also like to Read:
Crystal oscillator - Basics, Working, Frequency Response, Pros & Cons
Comparison between Synchronous Motor and 3-Phase Induction Motor
Electrical Braking System Advantages Limitations Disadvantages
Simple Arduino Project - Serial Communication Demonstration Project
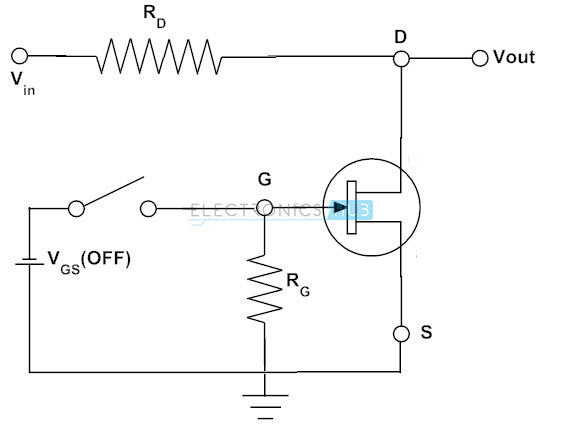
Advantages of FET | disadvantages of FET
This page covers advantages and disadvantages of FET. It mentions FET advantages or benefits and FET disadvantages or drawbacks.
What is FET?
Introduction:
FET is the short form of Field Effect Transistor.It is called unipolar transistor as current flow is carried out by majority charge carriers only.FET transistor is controlled by voltage rather than current unlike BJT.
Refer FET versus BJT >>.Following are the advantages of FET over BJT.
Based on the principle of operation and construction,FETs are classified as follows.
• JFET-Junction Field Effect Transistor
• MESFET-Metal Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor
• HEMT-High Electron Mobility Transistor
• MOSFET-Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor
Adobe illustrator cc mac crack.
Benefits or advantages of FET
Following are the benefits or advantages of FET:
➨High input resistance
➨Low noise figure
➨High efficiency as compare to BJT
➨Operating frequency range is higher compare to conventional BJT transistor.
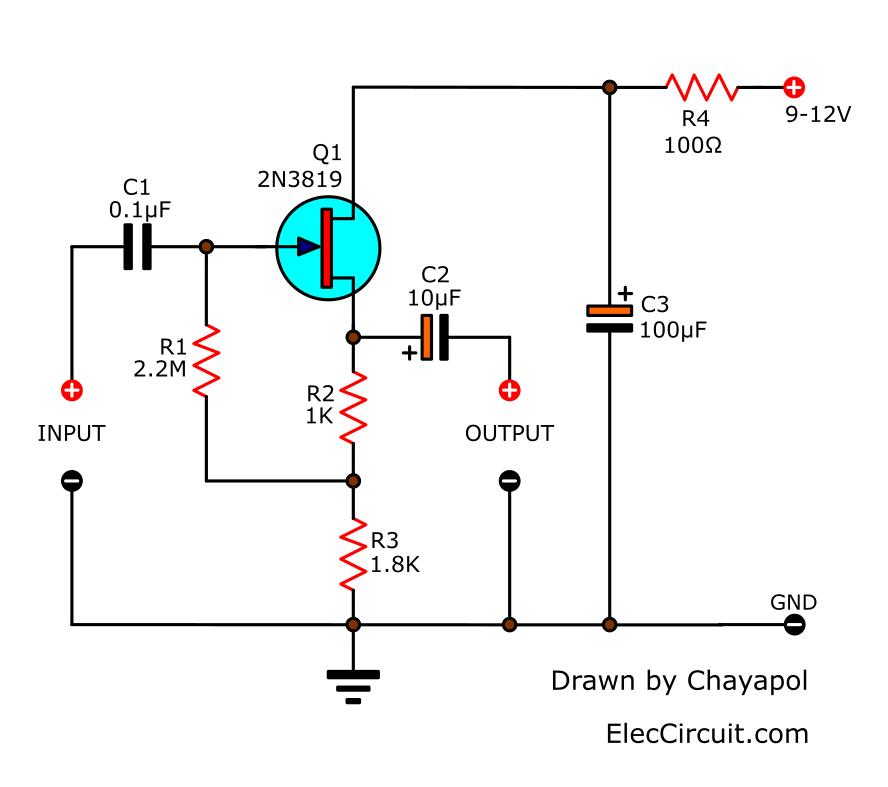
Drawbacks or disadvantages of FET
Following are the disadvantages of FET:
➨It has relatively lower gain-bandwidth product compare to BJT.
➨Transconductance is low and hence voltage gain is low.
➨FET has slower switching timescompare to BJT.The internal junction capacitance of FET is responsible forhigh delay times.
➨FET performance degrades as frequency increases.This is due to the feedback by internal capacitance.
➨They are more costly compare to junction transistors.
➨FET of MOSFET type is very susceptible to overload voltages,hence special handling is required during installation.
➨In MOSFET, the layer between Gate and Channel is very fragile which is vulnerable toelectro-static damage during installation. Once it is installed in a well designed circuit,there is no issue found.
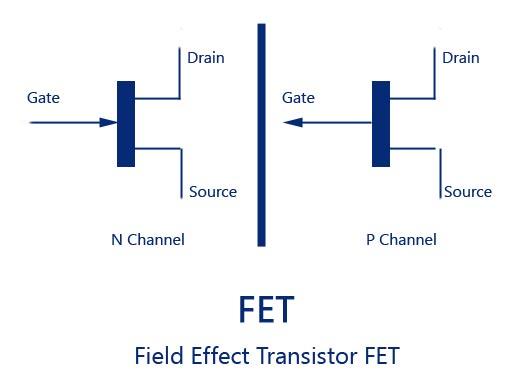
Advantages and Disadvantages of other wireless technologies
What is Difference between
difference between OFDM and OFDMA
Difference between SC-FDMA and OFDM
Difference between SISO and MIMO
Difference between TDD and FDD
FDMA vs TDMA vs CDMA
FDM vs TDM
CDMA vs GSM
RF and Wireless Terminologies
Share this page
Use Of Fetal Tissue In Research
Translate this page
